Aggregate Statement return a single value from the values in several lines of a column in a database table.
The value is calculated in the database system.
These Statement can be used with SELECT statement by specifying a column(column Field) of a database table as an argument.
Any number of column field can be used as arguments of aggregate Statement in SELECT statement.
Also multiple aggregate Statement can be used in a single SELECT statement.
Following are the aggregate Statement available in sap abap :
1 Average(AVG)
2 MAXIMUM(MAX)
3 Minimum(MIN)
4 Total(SUM)
5 Count(COUNT)
Average(AVG) :
Syntax : AVG([DISTINCT] field1) AVG determines the average value of the column field1 specified. It can only be applied to a numeric field.
Data types like DF16_DEC, D34_DEC (decimal floating point numbers ) , F(float) are recommended for the target fields.
Maximum(MAX) :
Syntax : MAX([DISTINCT] field1)
MAX determines the maximum value of the contents of the column field1 specified.
Minimum(MIN) :
Syntax : MIN([DISTINCT] field1)
MIN determines the minimum value of the contents of the column field1 specified.
Total(SUM) :
Syntax : SUM([DISTINCT] field1)
SUM determines the sum of contents of the column field1 specified.
This can only be applied to a numeric field
To avoid overflows it is recommended to make data type of target field greater than of the source field.
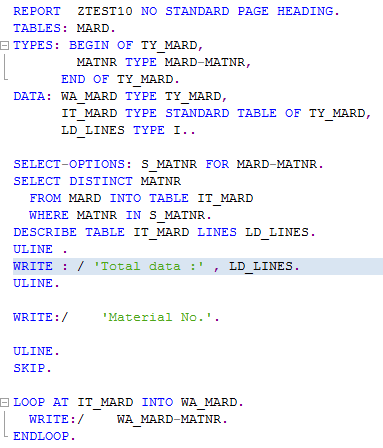
Count(COUNT) :
1. Syntax : COUNT(DISTINCT field1)
It determines the number of different values in the column field1 .
2. Syntax : COUNT( * )
It determines the number of rows in the result set. No column field field1 is specified in this case.
example : In the ekpo table we find MENGE field with PO number '3500014180'.
Output
Some interesting points about aggregate Statement :
1. When aggregate Statements are used,the SELECT statement bypasses SAP table buffering. It is a disadvantage if tables are buffered.
2. Columns of the type STRING or RAWSTRING cannot be used with aggregate Statement.
3. Pooled and Cluster tables do not any support aggregate Statement other than COUNT (*).
4. If the addition FOR ALL ENTRIES is used before WHERE , apart from COUNT(*) no other aggregate Statement can be used.